Reading Time: 15 mins

What: 50 hands-on Python coding challenges designed for beginners aged 8-15 to build programming skills through real projects.
Who: Kids eager to learn Python, parents seeking structured learning paths, and young coders ready to build confidence.
Why: Python is the #1 beginner-friendly language, opening doors to AI, game development, web apps, and high-paying tech careers.
When: Start today—these challenges progress from basic to advanced, perfect for learning at your own pace.
Where: Complete these anywhere with a computer and internet connection, whether at home, in coding classes, or summer camps.
How: Follow step-by-step challenges, write code, test projects, and build a portfolio of working programs.
Learning Python shouldn’t feel like homework. Yet most beginners quit within weeks because they’re stuck copying code they don’t understand or watching endless tutorials without building anything real.
Here’s what’s worse: Without hands-on practice, your child never discovers if coding is truly their passion. They miss the excitement of seeing their first program run, the confidence from solving real problems, and the skills that lead to future opportunities.
The solution? Start with Python coding challenges that feel like creative projects, not drills. These 50 challenges let kids build games, tools, and programs they’ll actually use—turning screen time into skill time while keeping parents informed every step of the way.
Keep reading to discover challenges your child can start today, organized by difficulty level with clear explanations anyone can follow.
Python coding challenges are bite-sized programming tasks that teach specific skills through hands-on building. Think of them as creative missions where your child writes real code to solve actual problems—from building a calculator to creating a simple game.
Why Python challenges work better than passive learning:
Python coding challenges transform abstract concepts into tangible results. When your child completes their first challenge, they don’t just understand variables—they’ve used them to build something that works.

Starting with Python challenges doesn’t require advanced knowledge—just curiosity and a willingness to experiment. Your child can begin today with these simple steps.
Before you start coding, set yourself up for success:
Download Python 3.12 or later from python.org. For beginners, we recommend Visual Studio Code or IDLE (included with Python)—both are free and beginner-friendly.
If you need help getting started, explore our guide on how to code in Python for detailed setup instructions.
Spend 2-3 days understanding:
Don’t worry about memorizing everything. You’ll learn as you code.
Pick your first challenge from the “Getting Started” section below. Read the description, try writing the code yourself, then test it.
When you get stuck (and you will):
Complete 2-3 challenges per week. Quality beats quantity—understanding one challenge fully teaches more than rushing through five.
Curious about what Python can do beyond these challenges? Check out what is Python used for to see real-world applications.
These challenges progress from simple to advanced, with each section building skills for the next. Start at your comfort level—there’s no wrong place to begin.
Skills: Variables, print(), input(), basic math
Print your name, age, and favorite hobby on separate lines.
Ask for two numbers, then display their sum, difference, product, and quotient.
Convert Celsius to Fahrenheit using the formula: F = (C × 9/5) + 32.

Calculate someone’s age based on their birth year and the current year.
Ask for a name, then tell the user how many characters it contains.
Print the multiplication table for any number from 1 to 10.
Determine if a number is even or odd.
Check whether an entered number is positive, negative, or zero.
Determine if someone can vote based on their age (18+).
Calculate simple interest using the formula: SI = (P × R × T) / 100.
Ask for favorite color, respond differently to specific colors.
Calculate circle area using πr². Use 3.14159 for pi.
Count down from 10 to 1, then print “Blast off!”
Ask for a name and number, then repeat the name that many times.
Convert percentage scores to letter grades (A, B, C, D, F).
Skills: Lists, while loops, string manipulation, basic functions
Create a list of 5 shopping items, then print them with numbers.
Generate random number 1-100, let user guess until correct.
Need inspiration? See how to make a simple password generator in Python for more practical projects.
Check if a word reads the same forwards and backwards.
Count how many vowels are in a sentence.
Check if password meets requirements (length, uppercase, numbers).
Add up all numbers in a list and display total.
Find the largest number in a list without using max().
Take any text and print it backwards.
Determine if a number is prime.
Calculate factorial of a number (5! = 5×4×3×2×1).
Print numbers 1-100, but “Fizz” for multiples of 3, “Buzz” for 5, “FizzBuzz” for both.
Count how many times each word appears in a sentence.
Shift letters by 3 positions to encode messages (A→D, B→E).
Play against computer with random choices.
For more game ideas, explore how to make Tic Tac Toe game in Python.
Print first 10 numbers in Fibonacci sequence (0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5…).
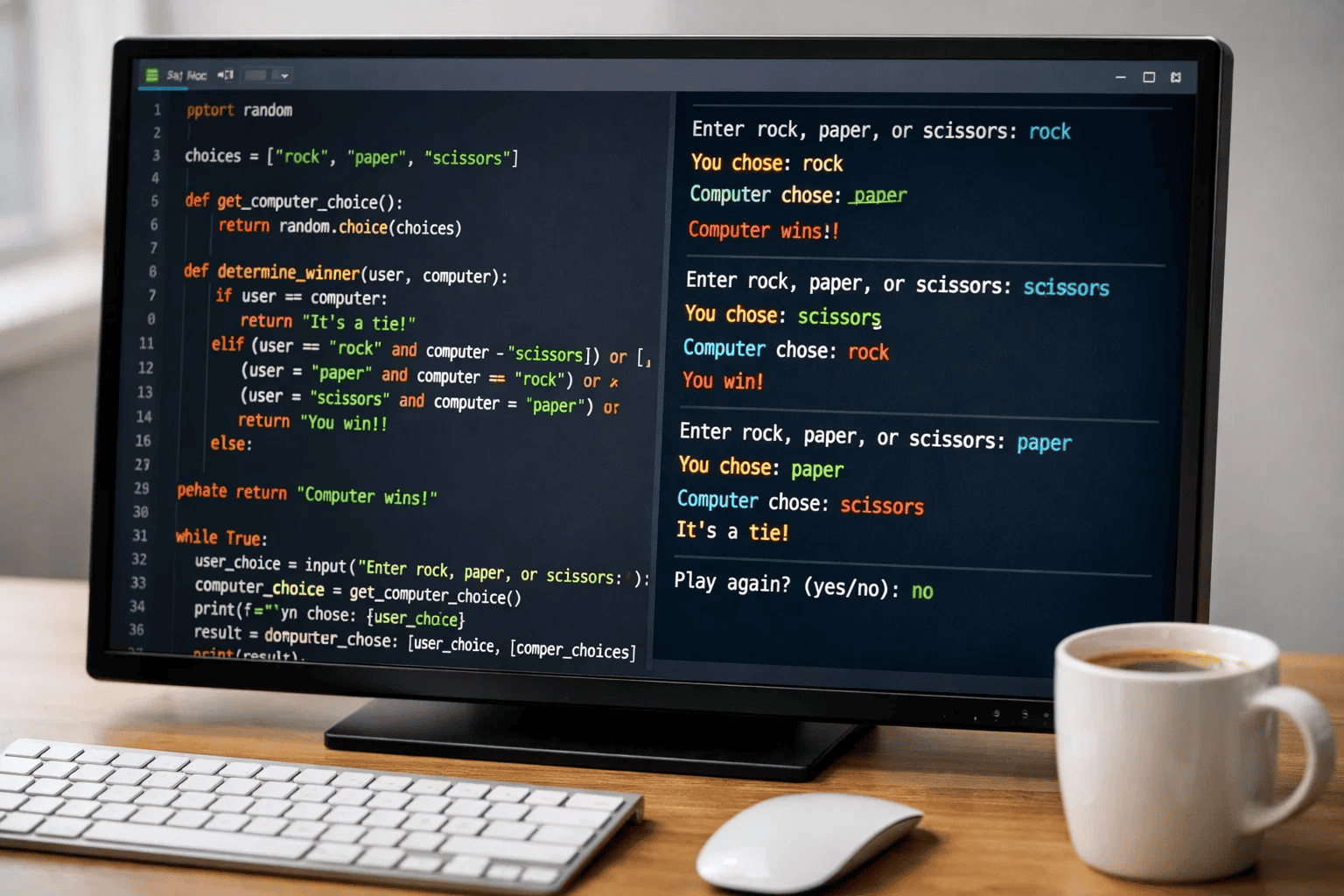
Skills: File handling, modules, basic OOP, practical applications
Create app to add, view, and remove tasks.
Save user notes to a text file and read them back.
Store names and phone numbers, search by name.
Ask 5 questions, track score, show results.
Create story with user-filled blanks (noun, verb, adjective).
Classic word-guessing game with lives system.
Calculate Body Mass Index and categorize results.
Simulate rolling dice any number of times.
Convert between units (km/miles, kg/pounds, etc.).
Create bot that responds to keywords.
Interested in AI? Learn how to make AI in Python to take chatbots further.
Skills: Classes, advanced algorithms, project integration
Create classic snake game with Pygame or Turtle.
Check out our guide on creating a snake game in Python for detailed steps.
Generate and solve a simple maze.
For maze game inspiration, see how to make a maze game in Python.
Build tic-tac-toe where computer never loses.
Create strong random passwords with options.
Track income and expenses with categories.
Fetch and display weather using free API.
Create functional stopwatch with start/stop/reset.
Generate RGB color, let user guess components.
Create CRUD operations with file storage.
Generate HTML page showcasing projects.

Even experienced coders make these mistakes when learning Python. Knowing them ahead of time saves hours of frustration.
The problem: Jumping to advanced challenges before mastering variables and loops.
Why it’s problematic: You’ll spend more time confused than coding. Each challenge builds on previous knowledge—skip the foundation and everything crumbles.
✅ Correct approach: Complete at least 10 Level 1 challenges before moving up. Boring? Maybe. Effective? Absolutely.
The problem: Seeing an error and immediately changing random code hoping it works.
Why it’s problematic: Python error messages tell you exactly what’s wrong and where. Ignoring them means solving the wrong problem.
✅ Correct approach: Read the last line of errors first—it’s usually the clearest. Google the error type with “Python” for instant answers.
The problem: Finding solutions online and pasting them without knowing how they work.
Why it’s problematic: You haven’t learned anything. The next challenge will be just as hard because you didn’t build the skill.
✅ Correct approach: Type code manually (don’t copy). Add comments explaining what each line does. If you can’t explain it, you don’t understand it yet.
The problem: Writing 50 lines of code, then running it hoping everything works.
Why it’s problematic: When errors appear, you won’t know which part failed. Debugging becomes overwhelming.
✅ Correct approach: Test after every 5-10 lines. Print variable values to see if they’re what you expect. Build confidence piece by piece.
The problem: Hitting a difficult challenge and switching to something else.
Why it’s problematic: Growth happens during struggle. Every coder faces these moments—pushing through is what separates learners from doers.
✅ Correct approach: Take a 10-minute break when stuck. Come back with fresh eyes. Still stuck? Ask for help—that’s what coders do.
The problem: Writing code without explanatory comments.
Why it’s problematic: When you return to the code next week, you won’t remember what it does or why you wrote it that way.
✅ Correct approach: Add comments above complex sections: # This loop counts vowels in the sentence. Future you will be grateful.
Python coding challenges aren’t just practice—they’re the foundation for skills that matter in school, careers, and life.
Transferable skills your child develops:
Breaking down challenges teaches systematic thinking. When faced with “make a calculator,” coders learn to ask: What inputs do I need? What processing happens? What output do I want?
This exact framework applies to math homework, science projects, and real-world problems. Your child becomes someone who tackles challenges instead of avoiding them.
Every error message is feedback, not failure. Python challenges normalize mistakes as part of the process.
Kids learn that “it didn’t work” means “what do I need to adjust?” instead of “I can’t do this.” This resilience mindset serves them far beyond coding.
Finishing a working program—even a simple one—builds genuine confidence. It’s tangible proof of capability: “I made this. It works.”
For more on building foundational skills, check our Python science fair project ideas that combine challenges with real presentations.
Python powers AI, data science, web development, and automation. Every challenge brings your child closer to industry-standard skills.
According to the Stack Overflow 2025 Developer Survey, Python remains the second most-loved language, with professionals earning average salaries of $120,000+. These challenges aren’t hypothetical—they’re practice for real careers.
Real outcomes from systematic practice:

Starting Python challenges requires minimal setup—most tools are free and run on any computer.
Essential tools every beginner needs:
Download from python.org (version 3.12 or newer). Works on Windows, Mac, and Linux. Installation takes 5 minutes.
Visual Studio Code: Professional-grade, beginner-friendly, with helpful extensions. IDLE: Comes with Python, simple interface perfect for learning. PyCharm Community Edition: Feature-rich, great for larger projects.
Pick one and stick with it for at least 20 challenges. Switching editors wastes time you could spend coding.
Not for writing code—for searching solutions when stuck. Every coder uses Google constantly. It’s a tool, not cheating.
Optional but helpful:
You don’t need expensive computers, paid software, or special equipment. If it can run Python, it’s enough.
Want to explore Python’s broader applications? Discover what Python is used for in real industries.
Python coding challenges transform curiosity into capability. Each completed project proves your child can build, solve, and create—not just consume screen time.
Key takeaways to remember:
The best time to start was yesterday. The second-best time is right now. Pick Challenge 1, write your first line of code, and watch what your child can build.
Want personalized guidance for your child’s coding journey? ItsMyBot offers industry-level courses that adapt to your child’s pace and potential, with progress updates keeping you informed every step of the way. Turn screen time into skill time—explore our coding programs today.
At a pace of 2-3 challenges per week, most beginners complete all 50 challenges in 4-6 months. This timeline allows for proper understanding rather than rushing. Level 1 challenges take 5-15 minutes each, while advanced challenges may require 60-90 minutes. Consistent practice matters more than speed—completing one challenge weekly with full understanding beats rushing through five without learning.
Kids aged 8-15 can start Python challenges with varying entry points. Ages 8-10 benefit from visual block coding first before transitioning to text-based Python. Ages 11-15 can dive directly into Python with Level 1 challenges. The key factor isn’t age—it’s reading comprehension and willingness to problem-solve. If your child can follow multi-step instructions and enjoys puzzles, they’re ready.
No programming knowledge is required for parents. These challenges are designed with clear instructions beginners can follow independently. Your role is encouragement, not technical support. When kids get stuck, help them find answers through Google searches or community forums—teaching resourcefulness matters more than providing solutions. Many parents learn alongside their children, making it a shared growth experience.
Challenges offer hands-on practice; classes provide structured curriculum and mentorship. Challenges work best for self-motivated learners who enjoy experimenting independently. Classes like those at ItsMyBot combine challenges with expert guidance, peer collaboration, and personalized feedback—accelerating progress for students who thrive with support. The ideal approach often combines both: use challenges for practice between class sessions.
Python is the primary language for AI and ML, making these challenges perfect preparation. Challenges teaching loops, functions, and data handling build the exact foundation needed for AI libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch. By Challenge 40, kids understand concepts like pattern matching and data processing—core AI principles. For deeper AI exploration, see our guide on how to make AI in Python.
Yes, with some limitations. Tablets can run Python through browser-based IDEs like Repl.it or Google Colab—perfect for basic challenges. Chromebooks support Python through Linux development environment (enable in settings). For advanced challenges requiring graphics or game development, a traditional computer works better. Most families find that any laptop purchased after 2018 handles all 50 challenges comfortably.
Getting stuck is part of learning—here’s how to help. First, encourage reading error messages carefully; they often explain the problem. Second, try breaking the challenge into smaller steps. Third, search “Python [specific problem]” on Google—someone has solved it before. If truly stuck after 20 minutes, move to a different challenge and return later with fresh perspective. Persistence builds resilience, but forcing through frustration creates burnout.
Completing all 50 challenges creates a solid foundation, but exceptional portfolios need original projects too. Use these challenges to build skills, then create 2-3 unique projects solving real problems you care about. For example, after Challenge 45 (Expense Tracker), build a custom version for your family’s specific needs. Original applications demonstrate creativity beyond following instructions—exactly what colleges seek. Consider entering projects in competitions for additional recognition.