Reading Time: 9 mins
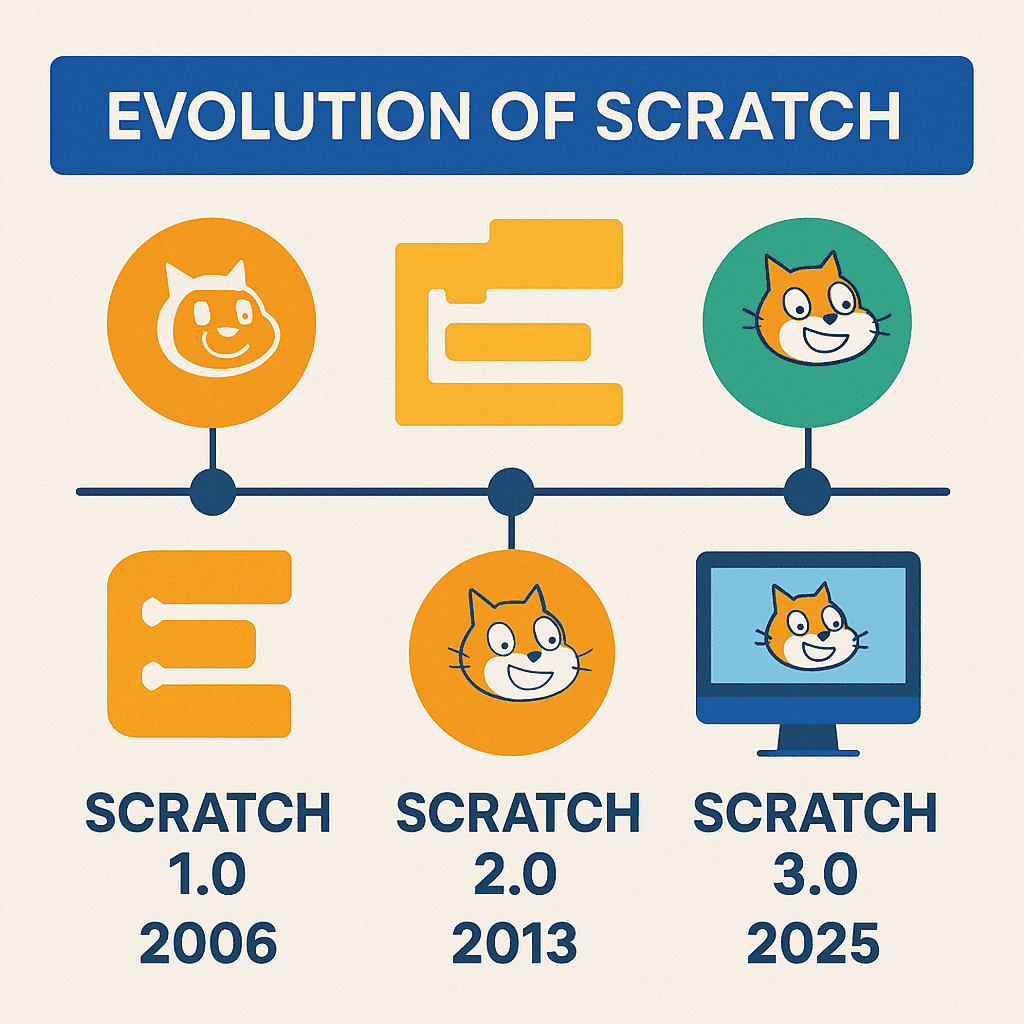
Have you ever wondered how old is Scratch and how this revolutionary programming platform transformed from a simple educational tool into a global phenomenon? The history of Scratch versions is a fascinating journey that spans nearly two decades, reshaping how children and beginners learn programming concepts.
Since its initial scratch release date in 2006, MIT’s Scratch has undergone significant transformations, each version introducing groundbreaking features that made programming more accessible to millions of users worldwide. From the original desktop application to the modern web-based platform, understanding this evolution helps us appreciate how far visual programming has come.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll walk you through every major Scratch version, exploring the key features, improvements, and the impact each release had on the programming education landscape. Whether you’re a teacher, parent, or coding enthusiast, this journey through time will give you valuable insights into one of the most influential programming platforms ever created.

The story begins in 2006, when MIT’s Lifelong Kindergarten Group, led by Mitchel Resnick, released the first version of Scratch. This inaugural release, known as Scratch 1.0, was a desktop application that introduced the world to visual programming through colorful, drag-and-drop code blocks.
During my years observing programming education, I’ve seen how Scratch 1.0 laid the foundation for what would become a programming revolution. The platform’s core philosophy—making programming as intuitive as playing with digital building blocks—was evident from day one.
The early adopters of Scratch 1.0 were primarily educators and students in computer science classrooms. Projects created during this era were relatively simple compared to today’s standards, but they demonstrated the platform’s potential for creative expression and logical thinking development.
The impact of Scratch 1.0 cannot be overstated. It proved that programming could be visual, intuitive, and fun—challenging the traditional text-based approach that had dominated computer science education for decades.
Following the success of Scratch 1.0, MIT released several incremental updates that refined the platform and added crucial features. The Scratch 1.4 release, in particular, became a milestone in the platform’s evolution.
By 2010, Scratch 1.4 had become the most stable and feature-rich desktop version of Scratch. This release included:

During this period, I witnessed the growth of the Scratch community from a few thousand users to over 100,000 active members. The platform’s educational impact was becoming undeniable, with schools worldwide adopting Scratch as their primary programming introduction tool.
The success of the 1.x series also highlighted some limitations of the desktop-only approach. Users wanted to access their projects from anywhere, collaborate in real-time, and share their creations more easily. These insights would drive the development of the next major version.
The Scratch 2.0 release in 2013 marked a revolutionary shift in the platform’s approach. For the first time, Scratch became available as a web-based application, fundamentally changing how users interacted with the platform.
The transition to web-based programming wasn’t just a technical upgrade—it represented a philosophical shift toward universal accessibility. Students no longer needed to install software or worry about system compatibility. They could start programming instantly from any device with internet access.
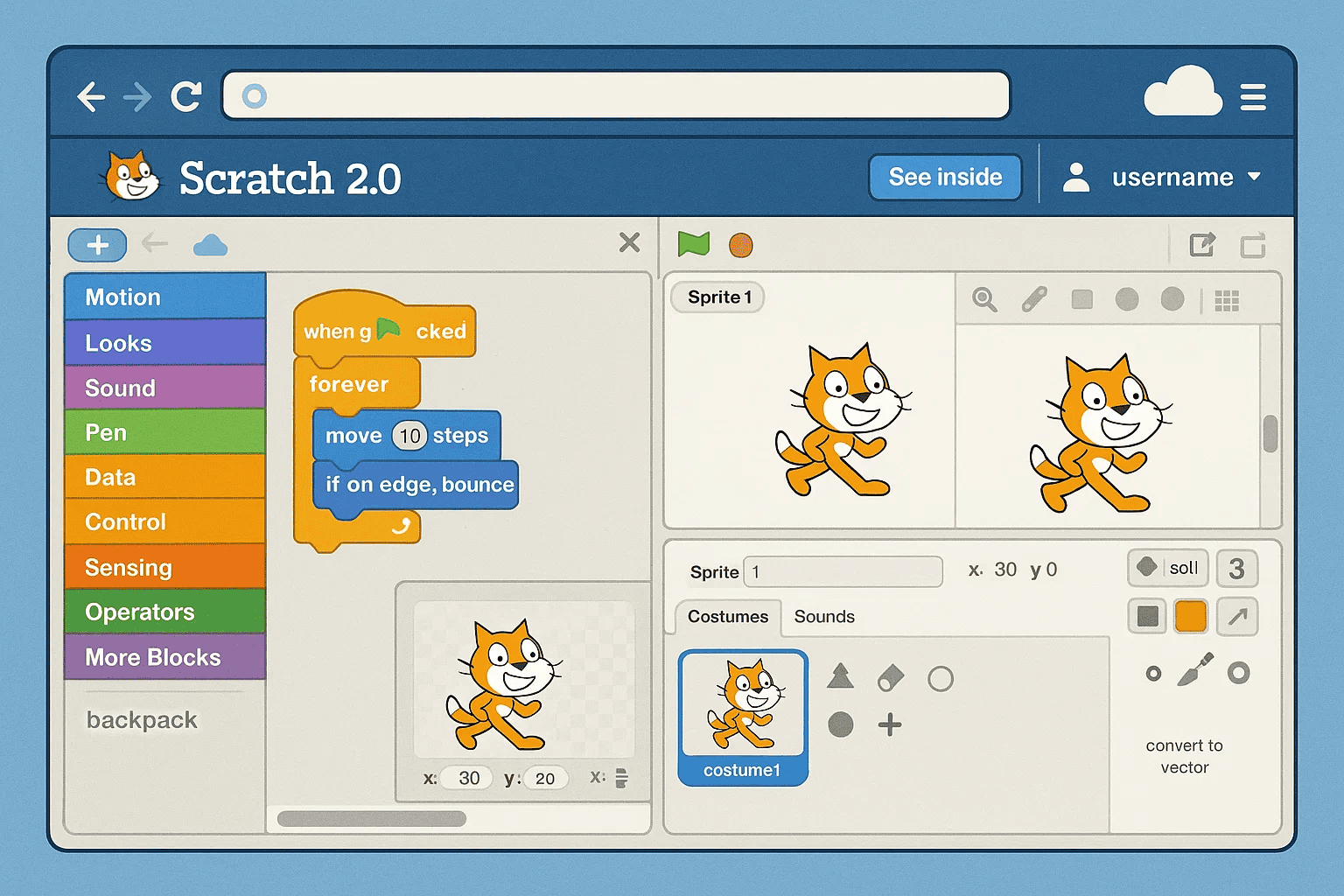
During my work with various educational institutions, I observed how Scratch 2.0’s web-based approach transformed classroom dynamics. Teachers could now easily:
The platform’s user base exploded from hundreds of thousands to millions of active users during the 2.0 era. This growth phase established Scratch as the leading platform for programming education globally.
For educators and students interested in exploring game development, our guide on how to make a flappy bird game on scratch demonstrates the advanced capabilities that became possible with Scratch 2.0.
The Scratch 3.0 release in January 2019 brought the platform into the modern era, addressing the limitations of Flash-based technology while introducing powerful new features. This version represents the current state of Scratch development and continues to be actively maintained and updated.

The Scratch 3.0 mobile support transformed how users interact with the platform. Students can now:
One of the most exciting aspects of Scratch 3.0 is its hardware integration capabilities. The extensions system allows connection to:
For students interested in creating interactive projects, our tutorial on how to make a mario game on scratch for beginners showcases the advanced capabilities of the current version.
As of 2025, Scratch 3.0 continues to receive regular updates and improvements. The development team actively maintains the platform, adding new features and addressing user feedback. Recent updates have focused on:
As of July 2025, Scratch 3.0 remains the current and actively maintained version of the platform. While there have been rumors and speculation about Scratch 4.0 or Scratch 5.0, MIT has not announced any concrete plans for a major version release.

The Scratch team follows a continuous improvement model rather than major version releases. Recent updates have included:
While no official Scratch 4.0 release date has been announced, the community speculates about potential future developments:
The Scratch community has grown exponentially, with over 100 million projects created and millions of active users worldwide. This growth drives continuous platform improvements and feature development.
For educators looking to maximize their use of the current version, our comprehensive guide on scratch coding for kids benefits and tips provides valuable insights into effective teaching strategies.
The history of Scratch versions represents more than technological evolution—it documents a fundamental shift in how we approach programming education. Each version has contributed to making programming more accessible, engaging, and effective for learners of all ages.
Multiple studies have demonstrated Scratch’s effectiveness in developing:
Scratch’s evolution has enabled its adoption in over 150 countries, with educational curricula specifically designed around the platform. The progression from desktop-only to web-based to mobile-compatible has removed barriers to access worldwide.
Many students who started with early Scratch versions have gone on to pursue careers in technology, demonstrating the platform’s effectiveness as a programming foundation. The skills developed through Scratch transfer effectively to professional programming languages and environments.
For students ready to advance their skills, our guide on how to create a snake game in python provides an excellent transition pathway to text-based programming.
Scratch was first released in 2006 by MIT’s Lifelong Kindergarten Group. The initial Scratch 1.0 version was a desktop application that introduced visual programming to the world.
There have been three major versions of Scratch:
As of 2025, Scratch 3.0 remains the current version, with continuous updates and improvements being released regularly.
While no official Scratch 4.0 release date has been announced, the MIT team continues to develop new features and improvements for the current version.
Most projects from Scratch 1.0 and Scratch 2.0 can be opened in the current version, though some features may need updating. The platform maintains backward compatibility for educational continuity.
Scratch was built using Squeak (a Smalltalk implementation) and drew inspiration from Logo, a programming language designed for education.
For more information about getting started with Scratch, visit our comprehensive guide on how to download scratch 3.
The history of Scratch versions tells a story of continuous innovation, educational impact, and community growth. From the pioneering Scratch 1.0 in 2006 to the modern Scratch 3.0 platform of today, each version has built upon the vision of making programming accessible to everyone.
As we look toward the future, Scratch continues to evolve, incorporating new technologies and pedagogical approaches while maintaining its core mission of empowering learners through creative coding. The platform’s journey from a simple desktop application to a global educational phenomenon demonstrates the power of thoughtful design and community-driven development.
Whether you’re a student taking your first steps in programming, an educator seeking effective teaching tools, or a developer interested in the evolution of educational technology, the Scratch version history offers valuable insights into how technology can transform learning.
The next chapter of Scratch’s story is being written by millions of users worldwide, each contributing to a platform that has fundamentally changed how we think about programming education. As new versions and features continue to emerge, one thing remains constant: Scratch’s commitment to making programming accessible, engaging, and fun for learners of all ages.
Related Reading: