Are you confused about the roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript in web development? You’re not alone. Many beginners struggle to understand how these three fundamental technologies differ and work together to create modern websites.
Without understanding these core differences, you might waste time learning the wrong skills first, feel overwhelmed by conflicting information, or build websites that look unprofessional and function poorly.
This comprehensive guide will clarify the unique role each technology plays, show you how they complement each other, and provide a clear learning roadmap to master web development in 2025.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language), CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), and JavaScript form the holy trinity of web development. Think of building a website like constructing a house: HTML provides the structural framework, CSS handles the interior design and aesthetics, and JavaScript adds smart home features and functionality.
In my 15 years of teaching web development, I’ve found that understanding this house analogy helps beginners grasp these concepts 10x faster than traditional technical explanations.
💡 Key Takeaway: HTML structures content, CSS styles appearance, and JavaScript enables interactivity. Each serves a distinct purpose but works together to create complete web experiences.
HTML serves as the backbone of every web page, defining the structure and content hierarchy. Created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1990, HTML uses markup tags to organize information into headings, paragraphs, lists, and other elements.
HTML creates the basic structure by:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>My First Website</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Blog</h1>
<p>This is my first blog post about web development.</p>
<ul>
<li>HTML structures content</li>
<li>CSS styles appearance</li>
<li>JavaScript adds functionality</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
HTML has evolved significantly with HTML5, introducing semantic elements like <header>, <nav>, <article>, and <footer>. These elements improve accessibility and help search engines better understand your content structure.
For comprehensive HTML guidance, check out our detailed HTML boilerplate guide and learn about div tags in HTML.
CSS transforms plain HTML documents into visually appealing websites. While HTML provides structure, CSS controls every aspect of visual presentation, from colors and fonts to layouts and animations.
CSS handles visual presentation through:
You can apply CSS in three ways:
<style> tags in the HTML headLearn more about how to link CSS to HTML for best practices.
/* External CSS file */
body {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
line-height: 1.6;
margin: 0;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
}
h1 {
color: #333;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
p {
color: #666;
font-size: 16px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
ul {
background: white;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 5px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
}
Modern CSS includes powerful features like:
Explore our guides on CSS shorthand properties and adding smooth hover effects to enhance your styling skills.
JavaScript transforms static websites into dynamic, interactive applications. Created by Brendan Eich in 1995, JavaScript enables real-time user interactions, data manipulation, and complex functionality.
JavaScript powers interactivity through:
JavaScript can be added to web pages through:
<script> tags// External JavaScript file
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function() {
// Get elements
const heading = document.querySelector('h1');
const button = document.querySelector('#myButton');
const list = document.querySelector('ul');
// Add click event
button.addEventListener('click', function() {
heading.style.color = '#007bff';
// Add new list item
const newItem = document.createElement('li');
newItem.textContent = 'JavaScript makes pages interactive!';
list.appendChild(newItem);
});
// Form validation example
const form = document.querySelector('#contactForm');
form.addEventListener('submit', function(e) {
const email = document.querySelector('#email').value;
if (!email.includes('@')) {
e.preventDefault();
alert('Please enter a valid email address');
}
});
});

Popular JavaScript frameworks include:
Learn about who developed JavaScript and explore loose vs strict equality in JavaScript to deepen your understanding.
Understanding the fundamental differences between these technologies is crucial for effective web development. Here’s a comprehensive comparison:
| Aspect | HTML | CSS | JavaScript |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Structure and content | Visual presentation | Functionality and interactivity |
| File Extension | .html | .css | .js |
| Language Type | Markup language | Style sheet language | Programming language |
| Learning Difficulty | Beginner-friendly | Intermediate | Advanced |
HTML Characteristics:
CSS Characteristics:
JavaScript Characteristics:
Based on my experience teaching over 500 students, I recommend this learning sequence:
This progression ensures solid fundamentals before tackling more complex concepts.
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript create powerful web experiences when combined effectively. Think of them as a three-piece orchestra where each instrument plays a crucial role in the final symphony.
HTML provides the foundation by establishing:
CSS enhances presentation by:
JavaScript adds intelligence through:
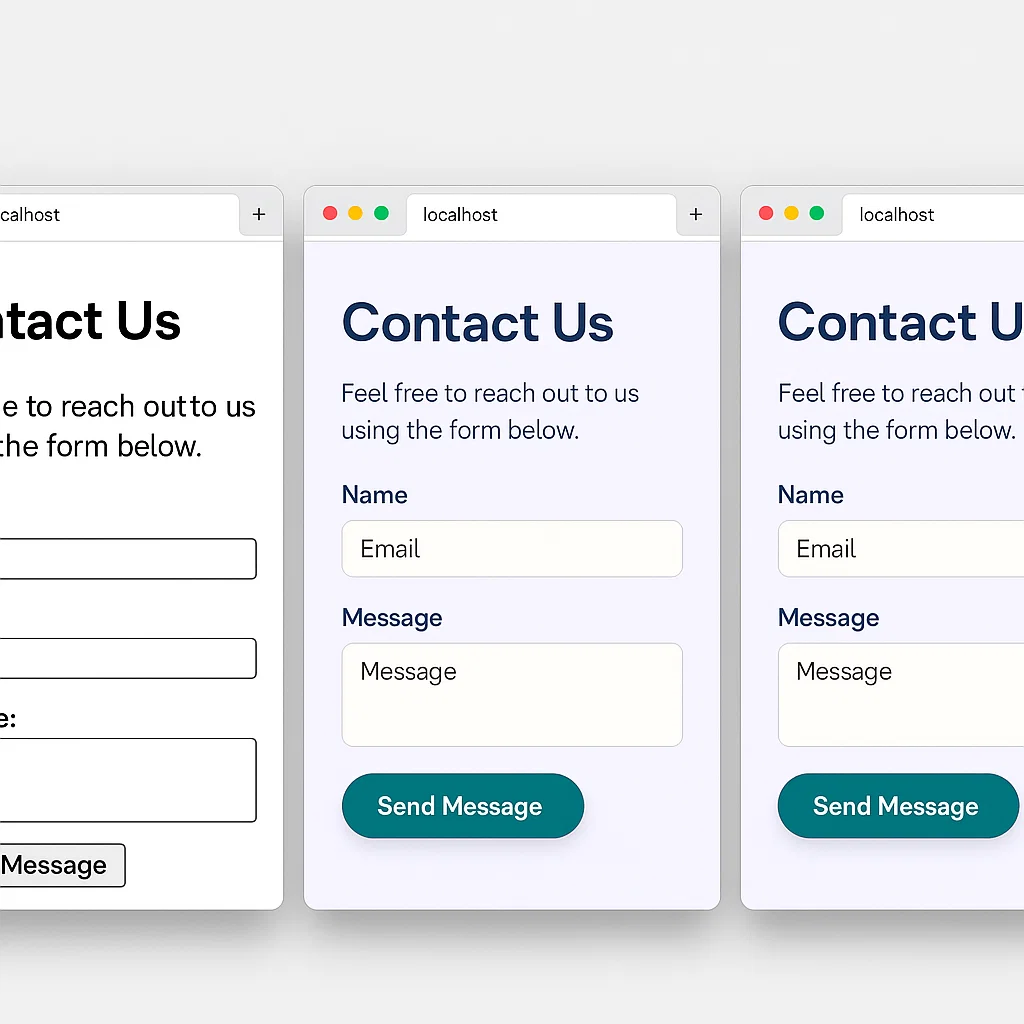
Consider a contact form that demonstrates all three technologies:
<!-- HTML: Structure -->
<form id="contactForm" class="contact-form">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" required>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" required>
<button type="submit">Send Message</button>
<div id="message" class="hidden"></div>
</form>
/* CSS: Styling */
.contact-form {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
background: white;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 10px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
}
.contact-form input, button {
width: 100%;
padding: 12px;
margin: 10px 0;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.hidden { display: none; }
.success { color: green; }
.error { color: red; }
// JavaScript: Functionality
document.getElementById('contactForm').addEventListener('submit', function(e) {
e.preventDefault();
const name = document.getElementById('name').value;
const email = document.getElementById('email').value;
const messageDiv = document.getElementById('message');
if (name.length < 2) {
messageDiv.textContent = 'Name must be at least 2 characters';
messageDiv.className = 'error';
} else if (!email.includes('@')) {
messageDiv.textContent = 'Please enter a valid email';
messageDiv.className = 'error';
} else {
messageDiv.textContent = 'Message sent successfully!';
messageDiv.className = 'success';
this.reset();
}
messageDiv.classList.remove('hidden');
});

Separation of Concerns: Keep HTML for structure, CSS for styling, and JavaScript for behavior. This approach improves maintainability and debugging.
Progressive Enhancement: Start with functional HTML, add CSS for visual improvement, then enhance with JavaScript for advanced features.
Performance Optimization:
For more integration techniques, explore our guide on adding attributes to JSON objects in JavaScript
Mastering HTML, CSS, and JavaScript opens numerous career paths in web development. Here’s a strategic approach to learning these technologies effectively.
Month 1-2: HTML Fundamentals
Month 3-4: CSS Mastery
Month 5-6: JavaScript Basics
Advanced CSS Topics:
Advanced JavaScript Concepts:
Front-End Developer: $75,000 – $120,000 annually
Full-Stack Developer: $90,000 – $150,000 annually
Web Designer/Developer: $55,000 – $95,000 annually
JavaScript Developer: $80,000 – $140,000 annually
Essential Tools for Web Development:
Recommended Learning Platforms:
Explore our comprehensive guides on best coding languages for game development and where to learn coding for beginners to expand your learning resources.
Create projects that showcase all three technologies:
For practical projects, check out our tutorials on creating a calculator using Python and building a simple password generator.
Image Placement 5: Insert image after the career opportunities section showing a modern developer workspace
Image Generation Prompt 5: “Create a realistic photograph of a modern web developer’s workspace from a slightly elevated angle. Show a clean desk with dual monitors displaying code editors with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files open. Include a laptop, smartphone for responsive testing, notebook with sketches, coffee cup, and some tech books. The monitors should show realistic code with syntax highlighting. Add soft natural lighting from a window and make the workspace look professional and organized with plants and modern furniture.”
Always start with HTML as it forms the foundation of web development. HTML provides the structural understanding necessary for CSS styling and JavaScript functionality. After mastering HTML basics (2-4 weeks), move to CSS for visual design skills, then progress to JavaScript for interactivity.
Yes, you can create a functional website using only HTML, but it will have limited visual appeal and no interactive features. HTML-only websites appear with default browser styling (Times New Roman font, basic colors) and lack modern user experience elements like animations, responsive design, or dynamic content updates.
While not absolutely required, I strongly recommend becoming comfortable with CSS before diving deep into JavaScript. Understanding CSS helps you manipulate styles programmatically with JavaScript and creates better user interfaces. Many JavaScript projects involve CSS modifications, so having solid CSS knowledge improves your development efficiency.
Front-end development involves HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create user-facing interfaces.
Back-end development uses server-side languages (Python, PHP, Node.js) to handle databases, server logic, and data processing. Full-stack developers work with both front-end and back-end technologies.
HTML: 2-4 weeks for basics, 2-3 months for advanced concepts
CSS: 1-3 months for fundamentals, 6+ months for advanced techniques
JavaScript: 3-6 months for basics, 1+ years for advanced programming concepts
Timeline varies based on learning intensity, prior experience, and practice frequency. Consistent daily practice accelerates learning significantly.
These three technologies provide a solid foundation for front-end web development. However, modern web development often requires additional tools:
Frameworks: React, Vue.js, Angular for complex applications
Build tools: Webpack, Parcel for project optimization
Version control: Git for code management
CSS preprocessors: Sass, Less for advanced styling
Backend languages: Python, PHP, Node.js for server-side functionality
Mixing concerns: Putting CSS styles directly in HTML or JavaScript
Ignoring semantics: Using divs for everything instead of semantic HTML elements
Browser compatibility: Not testing across different browsers
Accessibility: Forgetting alt text, proper heading hierarchy, and keyboard navigation
Performance: Not optimizing images, CSS, and JavaScript files
Learn from our guide on common coding myths for kids to avoid these pitfalls.
Always learn vanilla JavaScript first. Frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular are built on JavaScript fundamentals. Understanding core JavaScript concepts (variables, functions, DOM manipulation, events) makes learning frameworks much easier and helps you debug issues more effectively.
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript form the cornerstone of modern web development, each serving distinct but complementary roles. HTML structures your content, CSS makes it visually appealing, and JavaScript adds the interactive functionality that engages users.
Key takeaways from this guide:
The web development landscape in 2025 offers tremendous opportunities for those who master these fundamental technologies. Whether you’re aiming for a career as a front-end developer, full-stack engineer, or web designer, solid HTML, CSS, and JavaScript skills provide the foundation for success.
Start your journey today by practicing with simple projects, building your portfolio, and gradually tackling more complex challenges. Remember, every expert developer started exactly where you are now.
Ready to begin your web development journey? Explore our comprehensive tutorials on creating games in Scratch, Python programming basics, and building interactive applications to expand your coding skills.